What are INKT cells
The incidence of malignant tumors is increasing worldwide, and malignant tumors are becoming the main cause of death, which has become a global medical problem. Cellular immunotherapy, as an important part of the treatment system for malignant tumors, controls and kills tumor cells by stimulating the body's natural immune defense against tumors and rebuilding the immune microenvironment, bringing more treatment possibilities for the long-term survival benefits of patients with advanced malignant tumors, patients with tumors that have previously developed multidrug resistance, and patients with tumors that are prone to recurrence. Among them, the new generation of cell immunotherapy based on iNKT cells has shown good anti-tumor potential and is one of the cutting-edge research directions of anti-tumor therapy. It is expected to safely and effectively inhibit the deterioration, recurrence and metastasis of cancer, and meet the urgent treatment needs in the field of solid tumors.
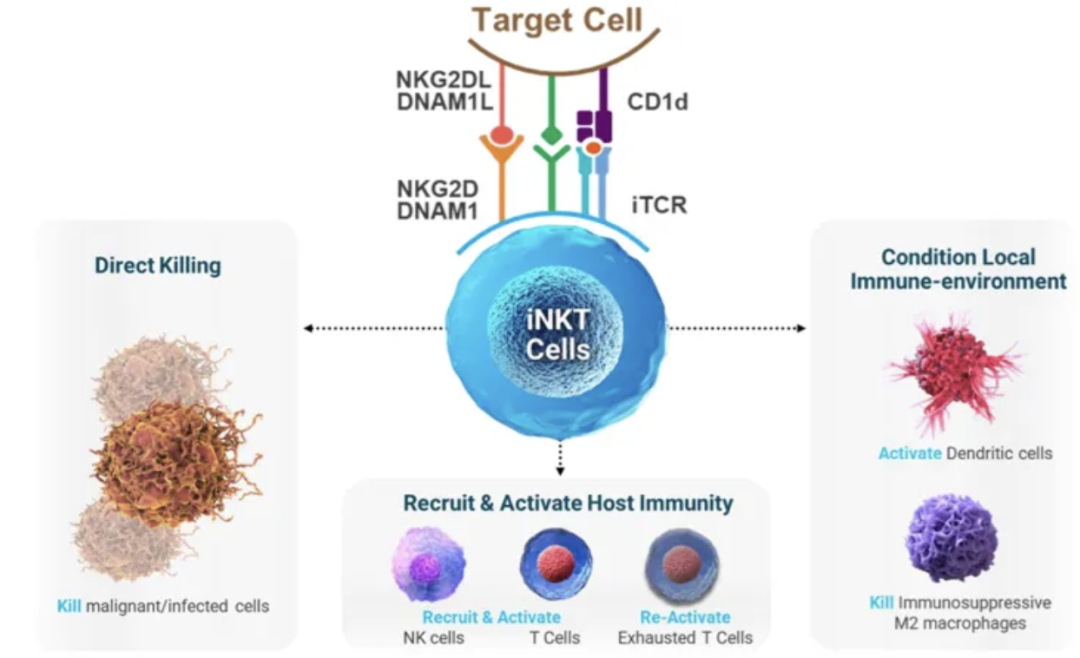
Invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT) are a unique T cell population that has different roles in coordinating immune responses and can be used for adoptive therapy. iNKT can recognize and kill abnormal cells, thereby enhancing protective immunity. iNKT deficiency increases the body's susceptibility to infection and cancer. agenT-797 is an allogeneic in vitro expanded iNKT cell therapy that is not donor-restricted and was originally developed for cancer treatment.
As a passive immunotherapy, adoptive cell therapy requires the separation of active immune cells from tumor patients, genetic engineering, functional identification and screening activation in vitro, and then amplification and re-infusion into the patient to achieve the purpose of tumor clearance. Depending on whether the effector cells express exogenous genes, adoptive cell therapy can be divided into two categories. One category requires genetic engineering of immune cells to improve the ability of immune cells to target tumor cells, such as chimeric antigen receptor modified T cells (CAR-T) therapy, T cell receptor chimeric T cells (TCR-T) therapy, and chimeric antigen receptor modified natural killer cell (CAR-NK) therapy. Another type is to directly isolate and screen tumor-infiltrating immune cells from the patient's peripheral blood or tumor tissue, such as tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TILs) therapy, cytokine-induced killer cell (CIK) therapy, lymphokine-activated killer cell (LAK) therapy, natural killer cell (NK) therapy, natural killer T cell (NKT) therapy, etc.
During viral infection, the number of iNKT cells in patients decreases rapidly, such as HIV patients after seroconversion. The antiviral activity of iNKT makes it potentially suitable as an adoptive immunotherapy for acute viral infections (including SARS-CoV-2 sequelae).
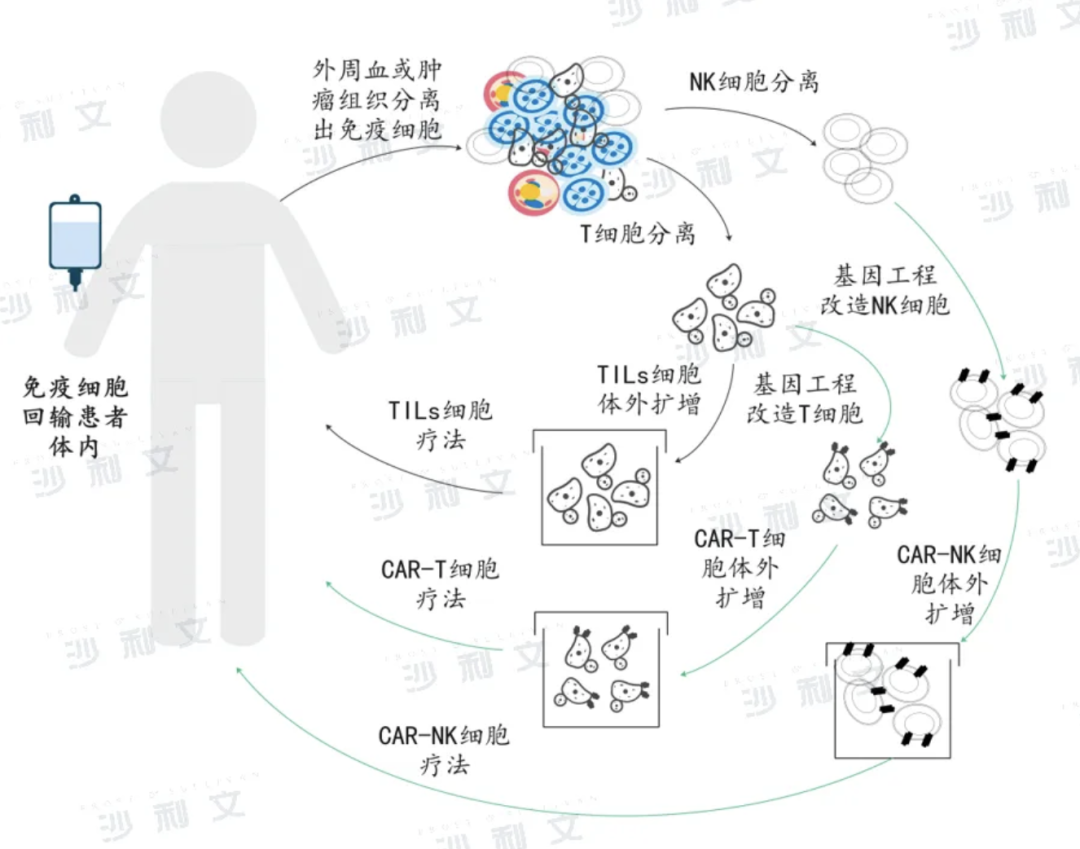
Above: Flow chart of adoptive cell immunotherapy
It is well known that the accumulation of senescent cells in the body drives the occurrence and development of diseases. There are many types of anti-aging drugs with different efficacy, but the complex targets make clinical application challenging. Interestingly, the endogenous immune surveillance system in the body can stop the accumulation of senescent cells through targeted clearance. However, the immune surveillance mechanism that mediates the clearance of senescent cells is still unclear.
As one of the earliest cell types to respond to pathogenic stimuli, invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells secrete cytokines with antiviral and anti-tumor properties. iNKT cells primarily recognize glycolipid antigens presented by the non-polymorphic MHC class I molecule CD1d. CD1d, which is usually expressed by antigen-presenting cells, is specifically expressed in aged preadipocytes, suggesting a potential link between aging and immune regulation.
Studies have found that the number and function of iNKT cells decrease with age.
How does iNKT work in the human body? Can agenT-797 be used to treat viral infections?
Academic journal reports
In February 2024, a research paper titled "A phase 1/2 clinical trial of invariant natural killer T cell therapy in moderate-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome" was published in the journal Nature Communications, analyzing the results of an open-label study of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) caused by SARS-CoV-2.

In the trial, 21 mechanically ventilated patients received agenT-797, with 3 patients receiving 100 million iNKT cells, 4 patients receiving 300 million, and 14 patients receiving 1 billion, all as a single infusion. No dose-limiting toxicity was observed.
AgenT-797 induced anti-inflammatory signals and did not induce cytokine release syndrome
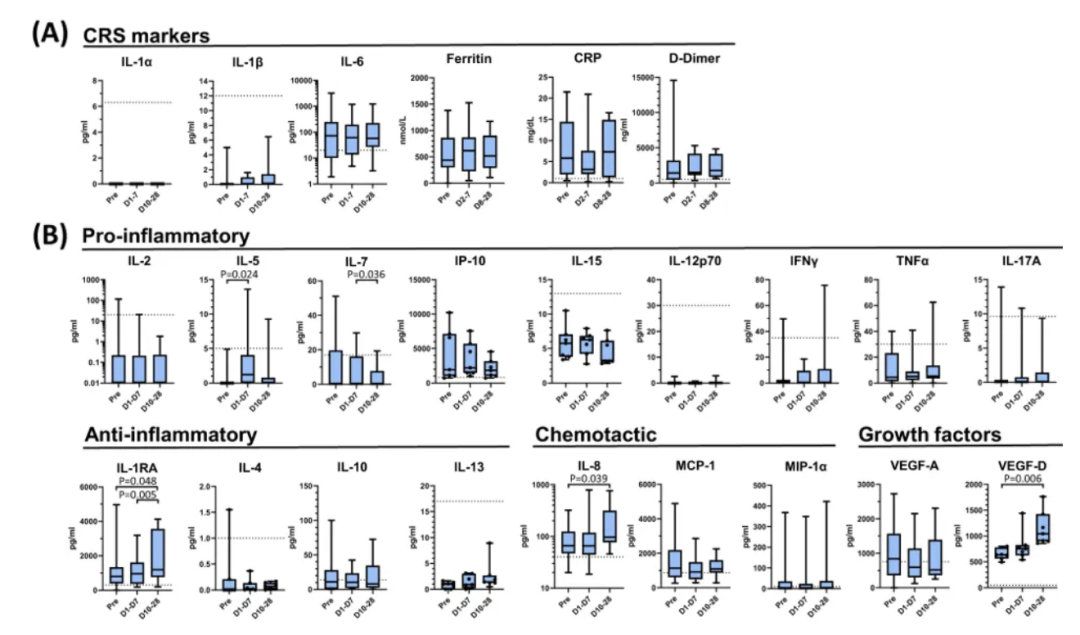
Acute phase clinical parameters and cytokines were measured in patients receiving agenT-797 over a 28-day period. Key indicators of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), especially IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, ferritin, C-reactive protein (CRP), and D-dimer levels, did not increase significantly (Figure A below).
IL-6, ferritin, CRP, and D-dimer levels were elevated before infusion, and decreased after infusion. After agenT-797 infusion, the serum biomarker IL-1RA showed the most significant increase (Figure B below), consistent with an increased anti-inflammatory response against IL-1-mediated cytokine release, while the level of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-7 was significantly reduced.
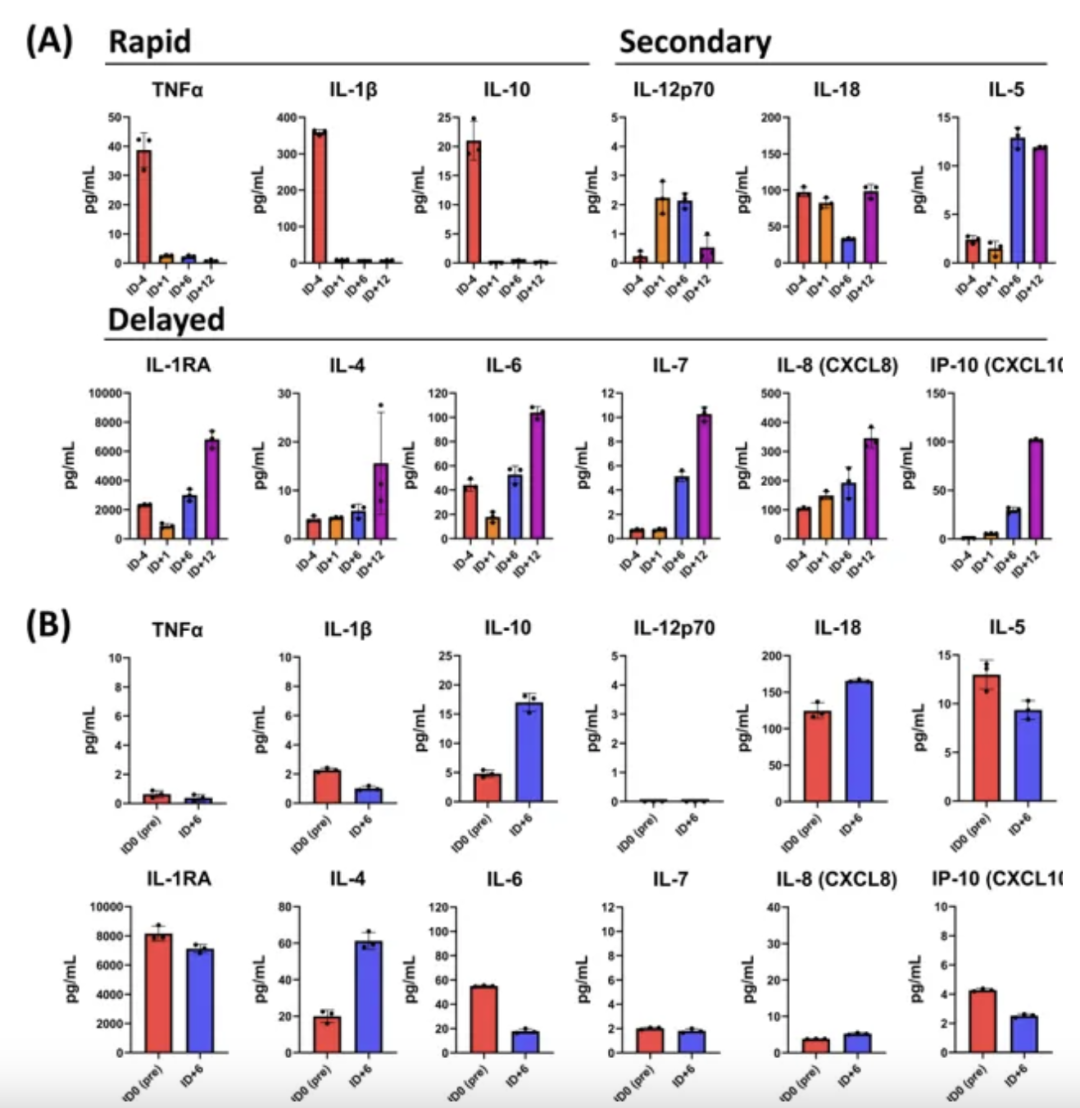
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and serum from EUA patients were used to assess changes in the lung cytokine profile (Figure below). After agenT-797 infusion, BAL key proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β and myeloid inhibitory cytokine IL-10 were reduced and sustained within 24 hours. Most changes in the cytokine profile after infusion were confined to the lung (BAL). iNKT interactions with M1 macrophages induced proinflammatory cytokine secretion, and interactions with M2 macrophages induced anti-inflammatory cytokine signatures. In a physiological setting, this interaction may be more subtle, and it can be speculated that agenT-797 in the inflamed lung modulates the activity of M1 and M2 macrophages, causing complex changes in lung cytokines (as observed in the figure below).
Persistence of AgenT-797
Based on digital droplet PCR of genetic markers unique to donor material, researchers measured the persistence of agenT-797 in patient PBMCs. AgenT-797 was still detectable in peripheral blood on day 6 after infusion, significantly higher levels were detectable at the highest dose level, and low levels may last longer (until day 28).
AgenT-797 activates both the adaptive and innate immune systems
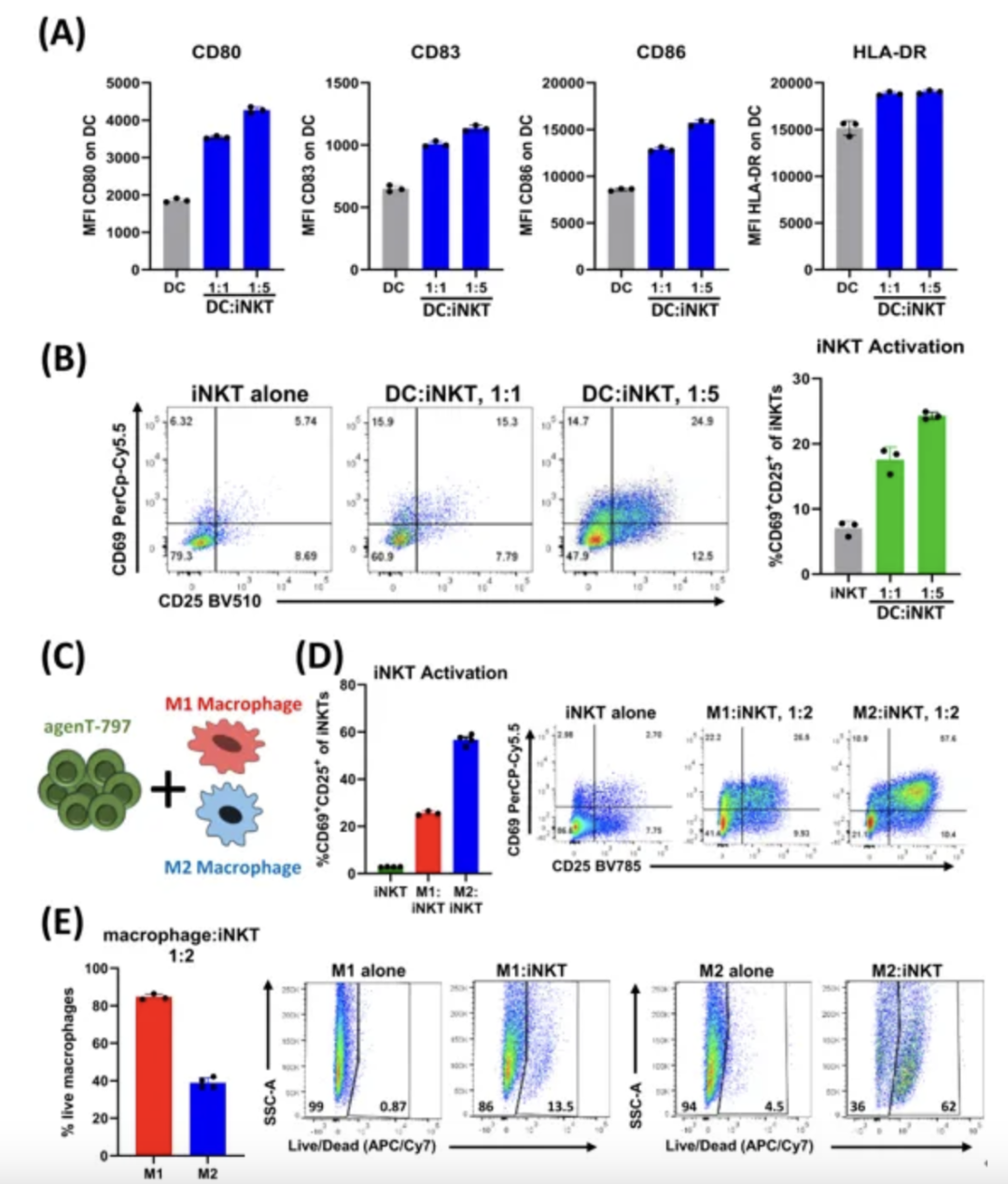
The researchers developed a co-culture assay to study the interaction between iNKT cells and myeloid cells. Dendritic cells and macrophages are key players in the innate response to infection. As shown in Figure A below, agenT-797 activated dendritic cells, which in turn caused further activation of iNKT cells (Figure B below). agenT-797 also directly interacted with M2 and M1 macrophages (Figures C, D below). M2 macrophages were observed to cause higher levels of iNKT cell activation and cytotoxic responses than M1 macrophages (Figures D, E below). Together, these features suggest a high level of crosstalk between iNKT cells and myeloid cells, which may be a key factor in the observed clinical responses, especially in reducing secondary infections.
Conclusion
This study found that agenT-797 can rescue exhausted T cells and rapidly activate innate and adaptive immunity. No dose-limiting toxicity was shown in 21 mechanically ventilated patients (including 5 patients receiving veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation VV-ECMO). Anti-inflammatory systemic cytokine responses were observed in the study, and the infused iNKT cells were persistent during follow-up, inducing only transient donor-specific antibodies. Clinical signals of associated survival and prevention of secondary infection were obvious.
In summary, cell therapy using Herun Medical iNKT cells is safe, can be rapidly scaled up, and can induce anti-inflammatory responses.






