The 21st century is the era of cell therapy, which provides new options for the treatment of intractable diseases. As we all know, our bodies are made up of cells, among which stem cells and immune cells are particularly worthy of attention.
Stem cells and immune cells work together to maintain human health, but many people still have questions, that is, what is the difference between stem cells and immune cells and what is the relationship between the two?
Different origins
Stem cells are a type of cell with self-renewal and multiple differentiation potentials. They have the potential to regenerate various tissues, organs and the human body. The medical community calls them "universal cells". According to the developmental stage of stem cells, they are divided into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Stem cells can be said to be at home everywhere. They can be seen in various tissues of the human body. Scientists first found stem cells in the bone marrow, which was once considered to be the birthplace of stem cells. As the research continues to deepen, researchers have discovered dental pulp stem cells in dental pulp and adipose stem cells in fat.
Immune cells refer to cells that participate in or are related to immune responses. They include lymphocytes, dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, mast cells, etc. Immune cells are responsible for clearing foreign pathogenic microorganisms, aging cells, mutant cells, and cancer cells.
Immune cells are born in the bone marrow, gradually grow in the thymus, and finally settle in various immune organs and blood of the human body, guarding the health of the human body at all times.
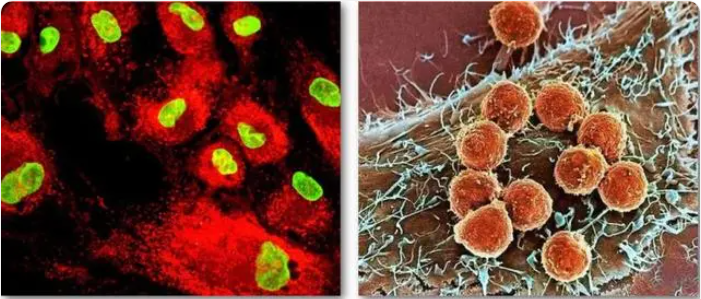
Stem cells (left), immune cells (right)
Different functions
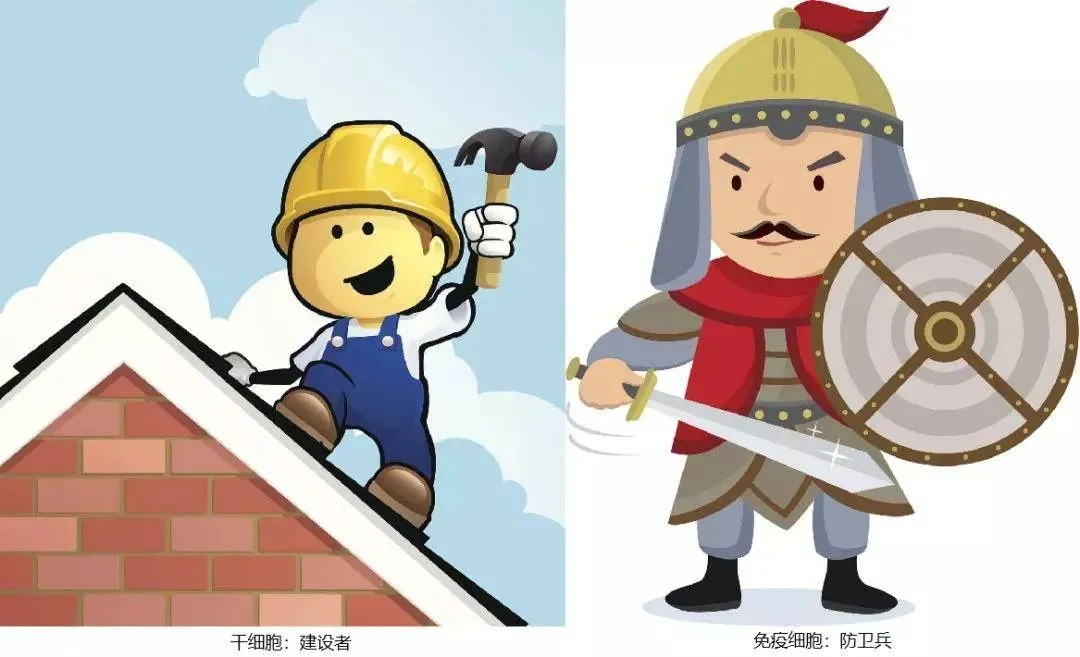
Image metaphor: stem cells are builders, immune cells are defenders.
If the human body is compared to a castle, then the importance of stem cells to the growth and development of life is like the basic raw materials such as steel and cement used in construction. It is the original cell that builds the human form, and through differentiation, it continuously provides new cells and develops into various types of tissues and organs in the human body according to needs.
After the framework is built, the subsequent maintenance work such as adding bricks and tiles is also supported by stem cells. Because of their abundant number and strong plasticity, they are also called "universal cells" in the medical field.
When the castle is completed, it is necessary to deploy a strong security system-the immune system. And immune cells are the core of the immune system. Many types of immune cells are stationed in different areas of the human body, each with its own duties, and together form a powerful "super marines".
When there is an invasion of foreign enemies, such as bacteria and viruses, the immune system will send combat soldiers to respond quickly and eliminate them. If there are traitors in the system, such as cancer cells, the front-line troops will take the initiative to attack, identify and eliminate them. However, when there are not enough members of the security system or there are too many traitors, many tasks cannot be completed, and our bodies will get sick.

Unfortunately, as we age, the number and capacity of stem cells and immune cells in our bodies will continue to weaken, and diseases will follow over time. Fortunately, scientists have developed biomedical technologies based on stem cells and immune cells to protect our health.
Different classifications
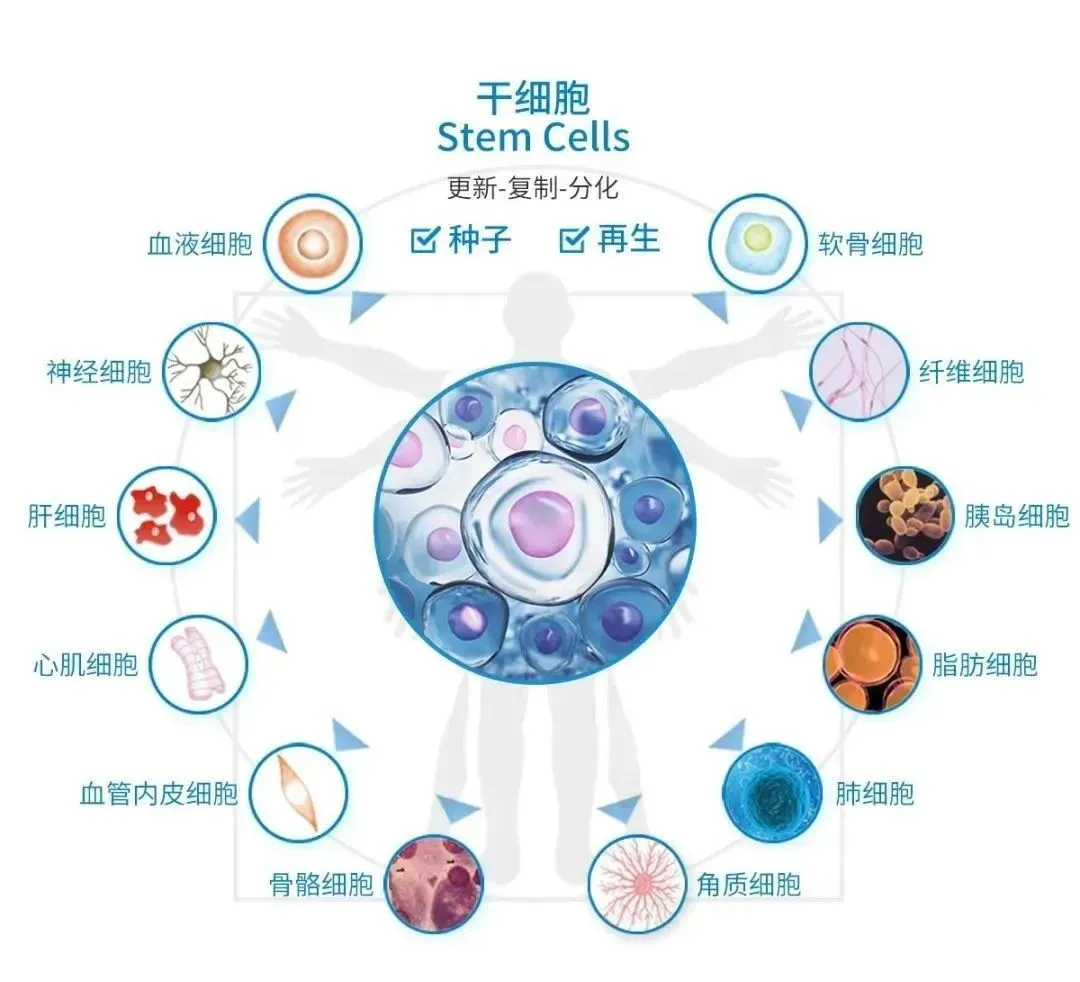
Stem cells
According to the different differentiation potentials, they are divided into totipotent stem cells, pluripotent stem cells, and unipotent stem cells;
According to the different developmental stages, they are divided into embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells;
According to the different sources of materials, they can be divided into bone marrow, fat, deciduous teeth, umbilical cord, umbilical cord blood stem cells, etc.;
According to the different tissue functions, they can be divided into hematopoietic, neural, myocardial, vascular, skin stem cells, etc.
Immune cells
Currently, the most commonly used clinical cells are natural killer cells (NK), cytokine-induced killer cells (CIK), and the recently popular CAR-T cells.
NK cells are inherent immunity and can remove aging and mutated cells in the body at any time, just like the police, maintaining social order at any time.
CIK further enhances the body's immunity and makes up for the relative lack of NK cells, just like when there are too many bad guys, the armed police need to be dispatched to help.
CAR-T is a genetically modified T cell. In the process of tumor cells being hunted by NK cells and CIK cells, some tumor cells learn to disguise themselves in the war and are no longer recognized by NK and CIK cells. So there is CAR-T, which can target and kill these cunningly disguised tumor cells. Therefore, CAR-T is like a special force with a clear mission, which can accurately annihilate the enemy.

Different extraction methods
Stem cells can be extracted from a variety of human tissues. Taking mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), which are currently the most widely used in clinical practice, as an example, they can also be extracted from a variety of human tissues such as the umbilical cord, fat, and dental pulp of newborns.
The main source of immune cells is blood, such as adult peripheral blood and infant umbilical cord blood. The blood contains a large number of mature immune cells, which circulate in our body to protect our health.

Different application directions
Stem cells
More inclined to tissue repair and chronic disease intervention, such as our physical trauma, liver cirrhosis, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes and its complications, the essence is that the cells of these tissues and organs are damaged, and stem cells are repairers. At this time, stem cells can be used to repair damaged tissues and organs.
Clinical research on stem cells involves hundreds of diseases, such as stem cell treatment of osteoarthritis, diabetic foot ulcers, Parkinson's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, reproductive system diseases, etc. At the same time, stem cells can also delay aging and prevent the occurrence of aging-related diseases.
Immune cells
Regulate sub-health: improve sub-health conditions such as poor sleep quality and memory loss, regulate the body's immunity, eliminate symptoms such as fatigue and physical weakness, and prevent diseases.
Delay aging: immune cells can efficiently identify and remove aging and apoptotic cells in the body, delay aging, and prevent the occurrence of aging-related diseases.
Improve chronic diseases: immune cells can activate the body's immune system, target and kill diseased cells, and improve chronic diseases.
Resistance to pathogenic microorganisms: Immune cells, especially NK cells, are natural weapons against viruses. Clinically, NK cells have been proven to be effective against a variety of viruses, including the new coronavirus, influenza A virus, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, etc.
Anti-cancer: Clear mutated cells in the body and prevent cancer cell proliferation.
Summary
In general: stem cells do "addition" and immune cells do "subtraction". Although stem cells and immune cells have many similarities and differences, they have many common characteristics and advantages in treating diseases and are both important components of the development of medical science and technology.
In the future, we believe that more amazing treatment methods and technologies will emerge in the research and application of stem cells and immune cells, making more important contributions to human health.






