Totipotent stem cells
Have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into any type of cells, and have the differentiation potential to form a complete individual.
For example, embryonic stem cells have morphological characteristics similar to early embryonic cells and strong differentiation ability. They can proliferate and differentiate into more than 220 types of cells throughout the body, and further form all tissues and organs of the body.
Sub-totipotent stem cells
Have the ability to produce multiple types of cells, but lose the ability to develop into a complete individual, and have a wider differentiation potential.
For example, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can differentiate into cells of various mesoderm tissues (such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, etc.) and cells of other germ layers (such as neurons).
Pluripotent stem cells
Have the ability to produce multiple types of cells, and their developmental potential is limited to a certain extent. They only differentiate into different cells of a certain type of tissue.
For example, hematopoietic stem cells, nerve cells, etc.
Unipotent stem cells
A type of cell in adult tissues and organs that can only differentiate in a single direction and produce one type of cell.
For example, stem cells in the basal layer of epithelial tissue and myoblasts in muscles are also called satellite cells. This tissue is in a stable state of self-renewal. However, if this tissue is damaged and requires multiple types of cells to repair, it is necessary to activate pluripotent stem cells to repair the injured tissue.
China Digital Science and Technology Museum Popular Science Stem Cells
CCTV13 reports on stem cell information
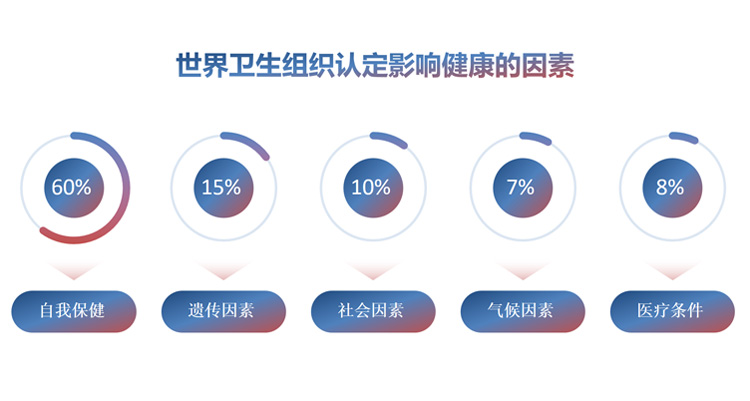

The World Health Organization has given a new definition of disease in the 21st century
All diseases and aging of the body are caused by damage, aging and death of cells in the body.
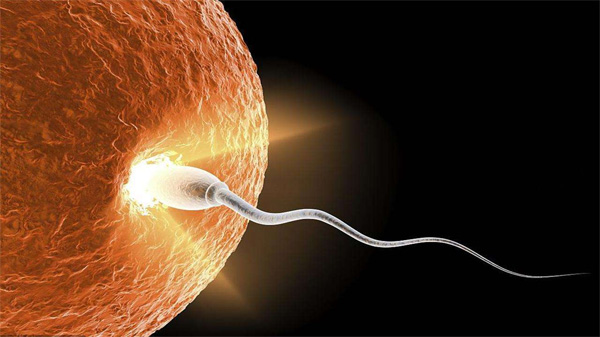
The fertilized egg is the first complete cell of life and the first stem cell of the human body
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are a type of cell with the ability to self-replicate and multidirectional differentiation. They can continuously renew themselves and transform into one or more cells that constitute human tissues or organs under certain conditions.
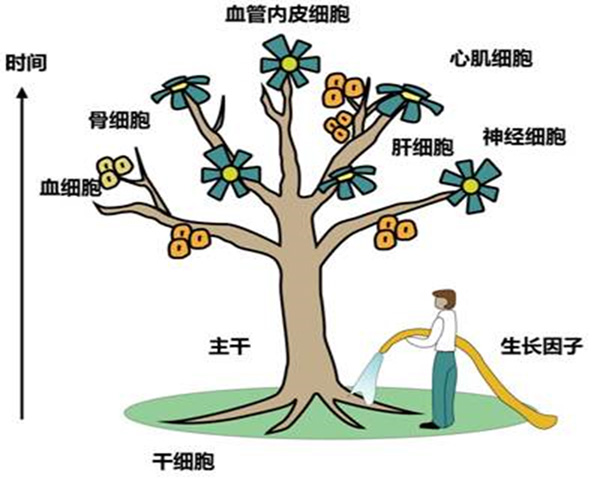
Functions of stem cells
Stem cells can differentiate into various functional cells, such as nerve cells, cardiomyocytes, muscle cells, liver cells, immune cells, etc.; they play a role in maintaining the metabolic balance of human cells, which helps the body repair, regenerate and delay aging.
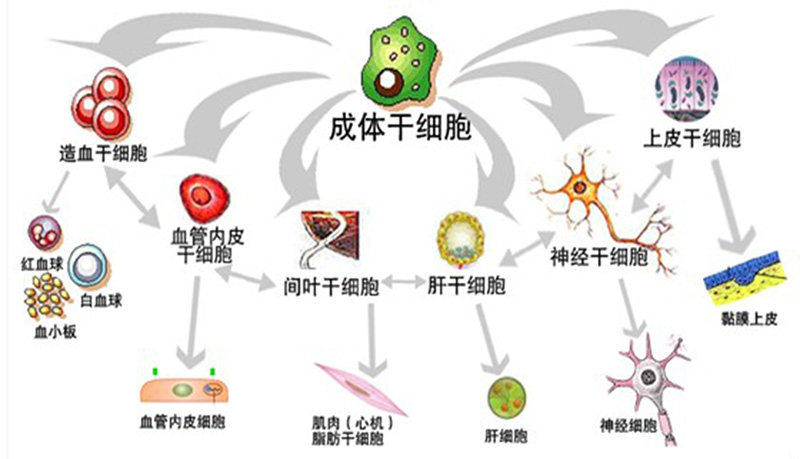
The importance of stem cells
Stem cells are primitive cells with unlimited self-renewal ability and multidirectional differentiation potential. They are the origin cells of the body and the primitive cells that form various tissues and organs of the human body.

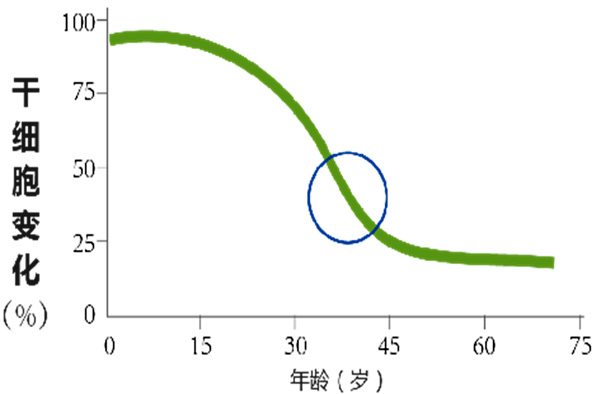
There are 6 billion stem cells when a person is born,
Only 1 billion at the age of 25
Stop growing and gradually ageing
Only 300 million at the age of 50
Aging accelerates
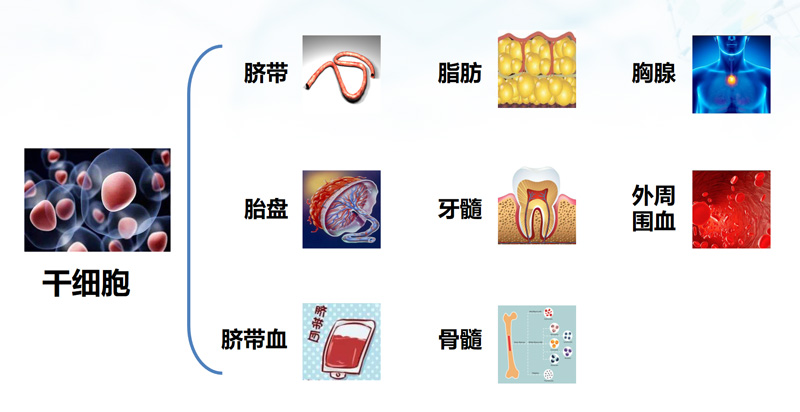
Classification of stem cells
Classification according to different differentiation potentials
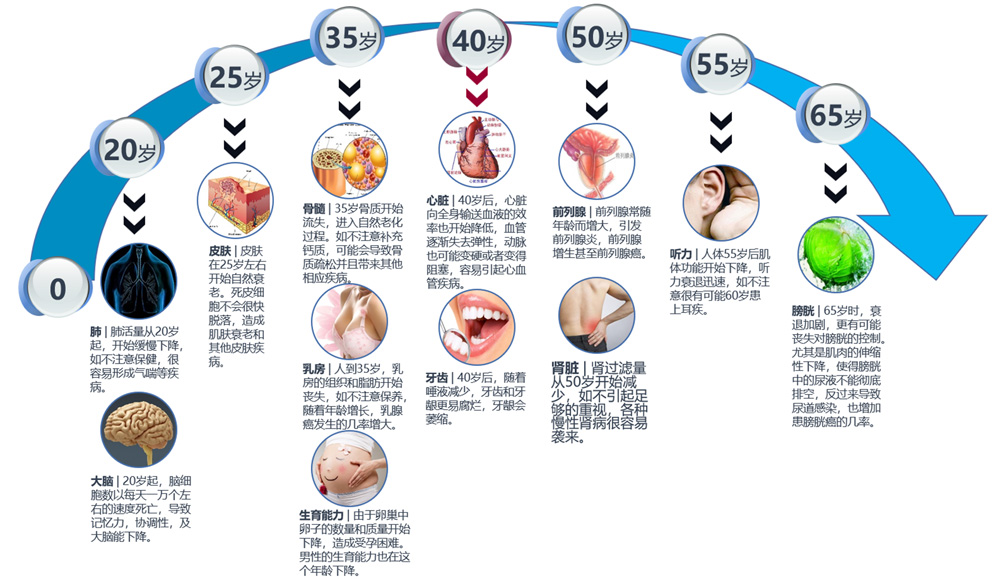
Simple diagram of the human aging process
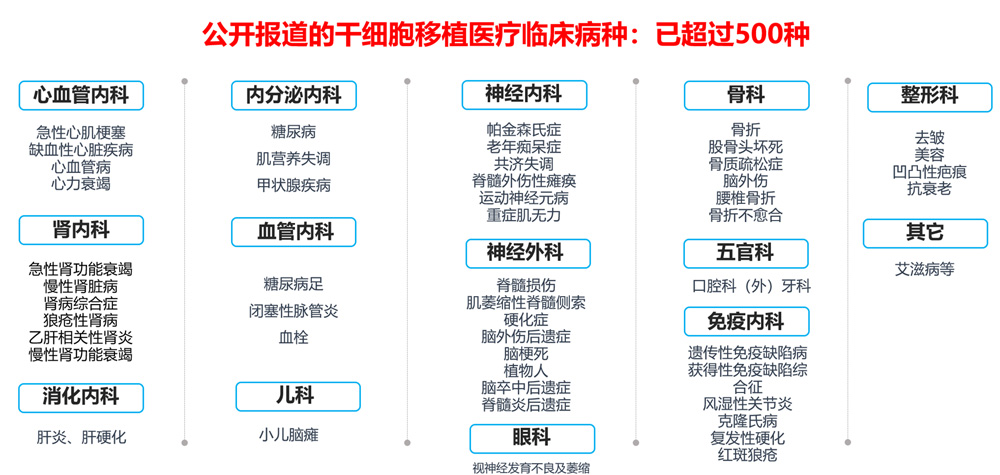
Stem cell treatment of diseases